Control valves Interview questions and answers
Question1. Why Do Different Control Valves Have Different Characteristics?
Answer :- Some valves have an inherent characteristic that cannot be changed, such as full port ball valves and butterfly valves. For other valve types, such as globe, the characteristic can be changed to suit the application.
- Ideally the inherent valve characteristic should be chosen to give an installed characteristic as close as possible to linear (see inherent vs installed characteristic). This enables the loop to remain tuned at all conditions with the same calibration settings.
Question2. Definition Of Linear And Equal Percentage Characteristic?
Answer :Linear – For equal stem movements the change of flow resulting from the movement is constant throughout the stroke.Equal Percentage – For equal stem movements the change of flow resulting from the movement is directly proportional to the flow rate immediately before the change took place.Besides the loop gain and installed characteristic considerations, equal percentage valve trim will generally give better rangeability and better control at low flow rates. Linear trim will give better control at flow rates over 50% of the valve capacity.Question3. What Is The Trim In A Control Valve?
Answer :The trim consists of the parts of the valve that affect the flow through the valve. In a standard globe valve the trim would just be the plug and seat. In a special valve the trim would consist of the plug, seat and retainer (or disk stack).Question4. Why Is Reduced Trim Required In Control Valves?
Answer :- Control valves are sized according to the application requirements and must satisfy both Cv and velocity criteria.
- Reduced trim is used where it is necessary for the valve to have a Cv capacity smaller than the maximum possible in that size of valve.
- The most common reason for reduced trim is that the flow rate is low for the size of valve required – particularly where 25mm valves have been specified as the smallest size to be used. Some plants stipulate that no control valve should be less than two sizes smaller than the line size, other that the valve should not be less than half the line size.
- The second reason is that on high pressure drop gas or vapour applications the valve invariably is sized on the outlet port velocity limits and the Cv required is much less than the full bore Cv.
Question5. What Is Meant By Critical Pressure And Critical Temperature?
Answer :Critical temperature is that above which a fluid cannot be liquefied by pressure alone. Critical pressure is the equilibrium or vapour pressure of a fluid at its critical temperature.Question6. Are Safety Valves, Regulators And Isolating Valves All Examples Of Control Valves?
Answer :Normally the term control valve is used to describe a valve that controls flow with an externally adjustable variable restriction. Safety valves and isolating valves should not be referred to as control valves without a qualifier such as safety control valve or on/off control valve. Regulators should be referred to as self-regulating control valves to avoid confusion.Question7. Is Flow Through A Control Valve – Turbulent Or Laminar?
Answer :- Flow through control valves is almost always turbulent.
- Laminar flow takes place with liquids operating at low Reynolds numbers. This occurs with liquids that are viscous, working at low velocities. Laminar flow in gases and vapours very seldom will be experienced in process plants.
Question8. What Is Cavitation?
Answer :Cavitation is a condition that occurs in liquid flow where the internal pressure of the liquid, at some point falls below the vapour pressure and vapour bubbles form and at some other point downstream rises above the vapour pressure again. As this pressure recovers so the bubbles collapse, and Cavitation takes placeIt is possible to predict where cavitation will occur by looking at the pressure conditions and the valve recovery factor. However, it is important to recognise that the damage that occurs is dependent on the energy being dissipated and is thus flow dependent.Cavitation sounds like stones passing through the valve.Question9. What Effect Does The Positioner Cam Have On A Valve Characteristic?
Answer :The feedback cam in the positioner controls the relationship between the control signal and valve position. With a linear cam at 50% signal the valve will be 50% open.It is possible to alter the apparent characteristic of a valve by changing the shape of the cam e.g. for a ball valve that has an inherent equal percent character it is possible to make it appear linear so that the flow rate through the valve at 50% signal is half of the maximum flow – the valve will however only be 25% open to achieve this result.From the control point of view there are advantages in doing this, but changing the valve characteristic and keeping the linear cam in the positioner is a better technical solution if it is possible.Question10. What Is Flashing?
Answer :Flashing is a condition that occurs with liquid flow where the pressure falls below the vapour pressure and remains below it. There are then two phases flowing (i.e. liquid and vapour) downstream.Severe damage can occur inside a valve due to erosion caused by the impact of liquid droplets travelling at high speeds.Question11. What Is Choked Flow?
Answer :- Choked flow (otherwise known as critical flow) takes place in a valve when an increase in pressure drop across the valve no longer has any effect on the flow rate through the valve. It occurs when the velocity of the gas or vapour reaches sonic (Mach 1) at the vena contracta.
- Choked flow is not necessarily a problem in valves but does need to be taken into account in the Cv calculations. For liquids, choked flow indicates the onset of full cavitation, which usually requires special steps to be taken to reduce damage.
- With clean gases there is no problem with choked flow. Use the choked pressure drop in any equation to calculate Cv or flow rates. High noise levels may be generated.
- Solid particles in gas flow will cause erosion due to the high velocities involved. With liquids full cavitation will occur when the flow is choked.
- High recovery valves, such as ball and butterfly, will become choked at lower pressure drops than low recovery valves such as globe which offer a more restricted flow path when fully open.
Question12. How Can Cavitation Damage Be Contained?
Answer :Three methods exist for treating cavitation in control valves – the first is to ensure that the plug and seat are made of a material that can resist the damage (e.g. stellite hard facing). The second is to control where the bubbles collapse and keep this away from vulnerable components (see Cav Control trim). The third is to control the pressure drop and velocities to ensure that the liquid pressure does not fall below the vapour pressure – thus eliminating cavitation altogether.Question13. How Can Flashing Damage Be Contained?
Answer :Flashing cannot be eliminated in the valve – if the downstream pressure is less than the vapour pressure then flashing will occur.To minimise the damage:-- Hard face trim (using hard facing materials such as Stellite, or Tungsten Carbide)
- Use more erosion resistant body material
- Increase size of valve, thus reducing the velocity
- Use angle valve – flow over plug
Question14. Definition Of Linear And Equal Percent Characteristics?
Answer :Equal Percent characteristics.The change of flow resulting from a fixed increment of valve travel is directly proportional to the flow immediately before the change took place.Linear characteristics.The change in flow resulting from a fixed increment of valve travel is constant throughout the whole stroke.General rules.- Use Equal Percent if in doubt.
- Use Linear for level control.
- Use Equal Percent for pressure control.
- Use Linear when the pressure drop across the valve is a large proportion of the total pressure drop.
Question15. How Is The Characteristic Determined In A Globe Valve?
Answer :There are several ways of altering the characteristic in a globe valve depending on the particular design.- The most common is to use the profile on the front of the plug head. In this case the seat ring and retainer are not changed. If the plug is cage guided the characteristic of the valve is usually determined by the retainer or disk stack with the plug having a flat face. As the plug moves up, it uncovers more flow paths.
- A series of small holes at the bottom of the retainer with larger holes at the top will give a bi-linear characteristic, which can be designed to give results similar to equal percent.
Question16. Is The Velocity Of A Fluid In A Control Valve Critical?
Answer :The velocity is one of the more important considerations in sizing a control valve. For long life on liquid applications the velocity at the exit of the valve body should be less than 10 m/s. This compares with generally accepted line velocities of about 3 m/s, which explains why control valves often are smaller than the line size.On gases and vapours the velocity at the exit of the valve body should be less than 0.33 Mach (1/3rd of sonic) for noise control valves and less than 0,5 Mach where noise is not a consideration.Question17. What Is The Difference Between A Liquid, A Vapour And A Gas?
Answer :These are all different states or phases in which a fluid can exist. H20 exists as a solid (ice), liquid (water), vapour (saturated steam), and a gas (superheated steam) – it depends on the temperature and pressure which phase is current. Practically the most significant difference between liquids and vapours/gases is the compressibility. Liquids are for most practical purposes incompressible where as the density of gas and vapours varies with pressure.Question18. What Is A Desuperheater And How Does It Differ From An Attemporator?
Answer :- A desuperheater is a device that is used to control the addition of water to superheated steam to reduce the temperature to within 10°C of saturation.
- An attemporator also adds water to steam to control its temperature but the set point temperature is higher and the downstream steam is still superheated.
- Generally desuperheaters are used in process plants where the steam is used for heating. Attemporators are used more in power stations for interstage temperature control.
Question19. What Is The Difference Between Installed And Inherent Characteristics?
Answer :The inherent characteristic is a plot of the flow rate through a valve (or Cv) against percentage opening with a constant pressure drop across the valve.This is the result of a workshop test where the upstream and downstream pressure are held constant and the only variables are the flow rate and opening of the valve.The installed characteristic is the plot of flow against opening using actual pressure drops experienced in practice. Due to the fact that in most applications the pressure drop increases as the flow rate drops, the installed characteristic will normally change from =% towards linear, and from linear towards quick opening.Question20. Why Are Control Valves Sometimes Very Noisy?
Answer :Noise is created by an object vibrating. Valve components will tend to vibrate whenever they are subjected to high velocity turbulent flow. Standard control valves will therefore tend to be noisy on high pressure drop applications particularly where flow rates are high, since the low pressure experienced downstream of the seat ring (at the vena contracta) is accompanied by very high velocities reaching as high as the speed of sound. Special low noise valves are designed to drop pressure gradually so that velocities are controlled at low levels.Question21. Can Two Control Valves Be Used In Series In High Pressure Drop Applications?
Answer :Dropping the pressure across two valves rather than one is theoretically better. However, in practice, the two valves will not usually control well together unless the process can operate with a very low proportional band with slow response times.A better, and usually less expensive approach is to use a valve that is designed with multiple pressure drop restrictions inside the trim.Question22. Can Two Control Valves Be Used In Parallel To Handle High Turndown Applications?
Answer :Two valves in parallel working on split range signals can give very high turndown capability. The situation that should be avoided if possible is that the larger valve operates in the “cracked open” position – one way to avoid this is to program the PLC or DCS to shut the small valve and use only the larger unit once the capacity of the small valve is exceeded.An alternative to two valves in parallel is to select a valve with a high rangeability such as a vee-ported ball valve.Question23. What Is The Difference Between Rangeability And Turndown?
Answer :Generally the term rangeability is used to describe the capability of a control valve (i.e. the ratio of the maximum Cv of the valve to the minimum Cv at which it can control) whereas the term turndown is generally used to describe the requirement of an application (i.e. ratio of Cv at maximum conditions to Cv at minimum condition).Note that the rangeability of a valve must be greater than the ratio of the Cv of the valve when fully open to the calculated Cv for the minimum conditions of the application.- Turndown applies to the application and is the ratio of the calculated Cv at maximum conditions to the calculated Cv at minimum
- Rangeability applies to the valve and is the ratio of the Cv of the valve fully open to the minimum Cv at which it can control
- The rangeability of the selected valve must exceed the turndown requirements of the application.
Question24. What Process Date Is Required To Size A Control Valve?
Answer :- Medium – What is passing through the valve? – if it is a special liquid give specific gravity (at flowing temperate), critical pressure, vapour pressure and viscosity.
- Pressures – What is the maximum pressure that the valve needs to be rated for? What are the upstream and downstream pressures for each of the maximum, normal and minimum flow rates.
- Flow rates – Maximum, normal and minimum. The maximum is used to select the valve size, the minimum to check the turndown requirement and the normal to see where the valve will control.
- Temperature – Maximum temperature for design plus temperatures at maximum, normal and minimum flow conditions.
- Please see the relevant enquiry sheets for additional information that may assist in the sizing and selection of the control valve required.
Question25. What Is Incipient Cavitation?
Answer :Incipient means “starting” – “incipient cavitation” begins when the pressure first dips below the vapour pressure and continues until the flow becomes choked at which point “full cavitation” is said to take place.Question26. What Is The Difference Between A Diffuser Plate And A Choke?
Answer :A diffuser is a plate with a large number of small holes in it that is installed in the downstream pipework. On gas and vapour applications it creates a back pressure between the valve and plate, and this enables a smaller value to be selected than would otherwise be possible, due to the lower velocity at maximum flow. The overall noise level produced will be lower as the overall number of pressure drop stages are increased.A choke is a restriction orifice and is a plate with one central hole. It is used with liquid flows and is also installed in the downstream pipe work to create backpressure. The purpose is to reduce the pressure drop across the valve at the maximum flow rate either to eliminate cavitation or to reduce the intensity of the damage to the valve.Question27. What Is A Field Reversible Actuator?
Answer :The actuators for many control valves are either spring-to-open or spring-to-close. The Mitech control valve actuator has all the parts necessary to reverse the action – this will normally take place in a workshop on site.Question28. Will Separable Flanged Valves Seal In A Pipeline?
Answer :The sealing face is part of the valve body and so the separable flanges are only there to hold the body in the line – they are not required to seal.Question29. What Is Vapour Pressure?
Answer :- The terms vapour pressure applies to a liquid, and is the natural equilibrium pressure that exists inside a closed vessel containing the liquid.
- Vapour pressure varies with temperature.
- The vapour pressure of water at ambient temperature of about 25°C is in the order of 4 kPa(a). This means that water will boil at 25°C if the external pressure is reduced to an absolute pressure of 4 kPa. At 100°C the vapour pressure of water is 101 kPa(a), which means that water will boil at 100° C at sea level where the atmospheric pressure is about 101 kPa(a).
Question30. Specific Gravity Is The Ratio Of The Density Of A Liquid To The Density Of Water – What Is The Specific Gravity Of Gas?
Answer :The specific gravity of gas is the ratio of the density of the gas to the density of air both measured at standard conditions of 101,3kPa and 15°C .Question31. What Is Meant By Cryogenic?
Answer :Cryogenic valves operate at temperatures below minus 100°C.These valves have extended bonnets to remove the stuffing box and actuator away from the source of cold and are made of materials such as stainless steel Monel or bronze that do not become too brittle at these temperatures.Question32. What Materials Can Be Used For Oxygen Service?
Answer :- Monel, bronze and austenitic stainless steel (e.g. 316) are the best materials for oxygen service in order of preference. The higher the velocity the better the material to be used.
- Velocities should not exceed 40 m/s in the valve body with Monel and bronze and should be less than 20 m/s with stainless steel.
Question33. Why Do Oxygen Valves Require De-greasing?
Answer :In the presence of most oils and greases oxygen will burn or explode. Even the oil deposited on a component by an uncovered hand is sufficient to cause a problem, which is why plastic gloves should be used when building degreased valves.Question34. Why Do Some Control Valve Actuators Have A Small Internal Fail Action Spring And Some Are External And Much Larger?
Answer :A piston actuator piped up double acting and operating with full supply pressure of about 500 kPa is very stiff and can normally operate satisfactorily with the flow direction either under the plug or over. This enables the flow direction to be chosen to assist with the fail action, which means that only a small bias spring is necessary inside the actuator to start initial movement in the right direction in the event of air failure. In the case of diaphragm actuated valves, the stiffness is much lower and so the flow direction must always be under the plug, resulting in the need of a heavy spring to give fail closed action. This cannot be fitted inside the actuator.Question35. Why Is Live Loading Sometimes Offered On Valves?
Answer :Live loading reduces the need for routine maintenance in the plant.Live loading is recommended on applications where a leak along the valve shaft would be likely to cause damage to the shaft and packing. High-pressure water and steam applications are examples of where live loading is advantageous.Question36. Why Is Energy Dissipation An Important Factor In Control Valve Selection?
Answer :All Control valves cause pressure drop in the fluid as it passes through the valve. Since pressure is a form of Potential Energy, this means that a certain amount of energy is converted from potential energy into some other form. The higher the Pressure Drop and the greater the flow rate then more energy will be dissipated. Depending on the type of valve and the trim design this energy can cause significant damage to valve components due to cavitations and high velocities, or can be environmentally unfriendly because of high noise levels produced. Through the careful choice of valve type and correct trim design it is possible to minimize the adverse effects of high levels of energy dissipation.
Friday, 11 May 2018
Control valves Interview questions and answers
Thursday, 3 May 2018
Instrumentation interview questions and answers
1.What is an Indicator?
An indicator is a human readable device that displays information about the process.


What is a Transducer?
A transducer is device that translates a mechanical signal into an electrical signal.
What is a Transmitter?
A transmitter is a device that converts a reading from a sensor or transducer into a standard signal and transmit that signal to a monitor or controller.


What Are The Primary Elements Usedfor Flow Measurement?
Answer :
The primary elements used for flow measurement are:
- Orifice Plate.
- Venturi tube.
- Pitot tube.
- Annubars.
- Flow Nozzle.
- Weir & Flumes.
- What Are The Different Types Of Orifice Plates And State Their Uses?
- Answer :The different types of orifice plates are:
- Concentric.
- Segmental.
- Eccentric.
CONCENTRIC: The concentric orifice plate is used for ideal liquid as well as gases and steam service. This orifice as a hole in concentric and hence known as concentric orifice.Eccentric & Segmental: The eccentric orifice plate has a hole eccentric. The use this is made in viscous and sherry flow measurement.The segmental orifice place has the hole in the form segment of a circle. This is used for colloidal and sherry flow measurement. What Is The Seal Liquid Used For Filling Impulse Lines On Crude And Viscous Liquid?
Answer :Glycol.How Do You Carry Out Piping For A Different Pressure Flow Transmitter On Liquids, Gas And Steam Services? Why?
Answer :Liquid lines: On liquid lines the transmitter is mounted below the orifice plate. Since liquids have a property of self draining.Gas Service: On gas service the transmitter is mounted above the orifice plate because Gases have a property of self venting and secondly condenlate formation.Steam Service: On steam service the transmitter is mounted below the orifice plate with condenlate pots. The pots should be at the same level.An Operator Tells You That Flow Indication Is More? How Would You Start Checking?
Answer :- First flushing the transmitter. Flush both the impulse lines. Adjust the zero by equalizing if necessary. If still the indication is more then.
- Check L.P. side for choke. If that is clean then.
- Check the leaks on L.P. side. If not.
- Calibrate the transmitter.
How Do You Do A Zero Check On A D.p. Transmitter?
Answer :Close one of the valve either H.P. or L.P. open the equalizing valve. The O/P should read zero.-
A solenoid is electrically operated valve. It consists of solenoid coil in which magnetic plunger moves. This plunger is connected to the plug and tends to open or close the valve. There are two types of solenoid valves:
1. Normally Open
2. Normally closed
Use: It is used for safety purpose in different electric work -
Types of bourdon tubes:
1. C type
2. Spiral
3. Helix -
Primary elements of measuring pressure are:
a. Bourdon Tube
b. Diaphragm
c. Capsule
d. Bellows
e. Pressure springs
These elements are known as elastic deformation pressure elements. -
Valve positioner can be used for following reasons:
a. Quick action
b. Valve hysterisis
c. Viscous liquids
d. Split range.
e. Line pressure changes on valve
f. Bench set not standard
g. Reverse valve operations -
Pressure gauge includes following components:
a. ‘C' type bourdon tube.
b. Connecting link
c. Sector gear
d. Pinion Gear
e. Hair spring
f. Pointer
g. Dial
Use of hair spring: Hair spring is responsible for controlling torque. It is also used to eliminate any play into linkages. -
excessive pressure to your differential pressure transmitter, you could damage your instrument. This is known as over-ranging the transmitter.
A three-way manifold valve is a device that prevents the instrument from being over-ranged. It also allows the isolation of the transmitter from the process loop (an option which could be used generaly for maintenance or re-calibration or fitting new equipment).
Monday, 9 October 2017
How to connect Mobile internet to PC via USB
How to connect Mobile internet to PC via USB
I Will show the Mobile internet to PC via USB in My Mobile Xiaomi MI MAX
1. First step connect your mobile with PC via USB
2. In the screen USB option will display in that you select charging only mode

3.In the above Picture you can see the SETTINGS folder click the settings
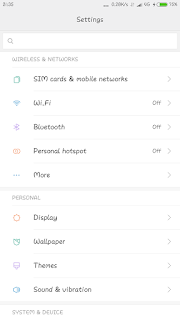
4. In the Above picture From wireless network go into more option menu
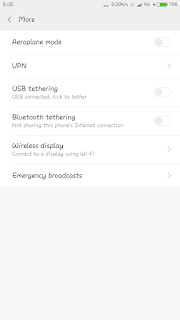
5. From the above picture you can see the Option USN Tethering so click to ON & also then ON the mobile data
6. Now go to your Browser in PC like Chrome, Firefox etc & checked the internet will work in Pc smoothly
7. I think it will work for all the Android phones.
Thank you
please share the content to your friends & family
I Will show the Mobile internet to PC via USB in My Mobile Xiaomi MI MAX
1. First step connect your mobile with PC via USB
2. In the screen USB option will display in that you select charging only mode

3.In the above Picture you can see the SETTINGS folder click the settings

4. In the Above picture From wireless network go into more option menu

5. From the above picture you can see the Option USN Tethering so click to ON & also then ON the mobile data
6. Now go to your Browser in PC like Chrome, Firefox etc & checked the internet will work in Pc smoothly
7. I think it will work for all the Android phones.
Thank you
please share the content to your friends & family
Friday, 14 July 2017
SSC Combined Graduate Exam Question & Answer for the Year 2014&2015
SSC Combined Graduate Exam Question & Answer for the Year 2014&2015
Please Click the bleow link & down load
https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B-MSgEVfiXVINmJrZFRURVFsN0U
Please Click the bleow link & down load
https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B-MSgEVfiXVINmJrZFRURVFsN0U
Friday, 7 July 2017
SSC Combined Graduate Level Exam Q&A
SSC Combined Graduate Level Exam Q&A
Please Click the below link & download
https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B-MSgEVfiXVINmJrZFRURVFsN0U
Please Click the below link & download
https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B-MSgEVfiXVINmJrZFRURVFsN0U
Sunday, 25 September 2016
# COMMON QUESTION ASKED @ ANY INTERVIEW #
# COMMON QUESTION ASKED @ ANY INTERVIEW #
Please click this below video link
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gnqzM6FWgTE
Tuesday, 30 August 2016
History of India Question & Answer
History of India Question & Answer
1. Where is the Indus Civilization city Lothal ?
(A) Gujarat
(B) Rajasthan
(C) Punjab
(D) Haryana
Ans : (A)
(A) Gujarat
(B) Rajasthan
(C) Punjab
(D) Haryana
Ans : (A)
2. Mohenjo Daro is situated in—
(A) Sindh Province of Pakistan
(B) Gujarat
(C) Punjab
(D) Afghanistan
Ans : (A)
(A) Sindh Province of Pakistan
(B) Gujarat
(C) Punjab
(D) Afghanistan
Ans : (A)
3. Which deity was not worshipped by the Vedic Aryans ?
(A) Indra
(B) Marut
(C) Varun
(D) Pashupati
Ans : (D)
(A) Indra
(B) Marut
(C) Varun
(D) Pashupati
Ans : (D)
4. The Vedanga consists of the—
(A) Kalp, Shiksha, Nirukta, Vyakaran, Chhanda, Jyotish
(B) Kalp, Shiksha, Brahman, Vyakaran, Chhanda, Jyotish
(C) Kalp, Shiksha, Nirukta, Aranyak, Chhanda, Jyotish
(D) Kalp, Upanishad, Nirukta, Vyakaran, Chhanda
Ans : (A)
(A) Kalp, Shiksha, Nirukta, Vyakaran, Chhanda, Jyotish
(B) Kalp, Shiksha, Brahman, Vyakaran, Chhanda, Jyotish
(C) Kalp, Shiksha, Nirukta, Aranyak, Chhanda, Jyotish
(D) Kalp, Upanishad, Nirukta, Vyakaran, Chhanda
Ans : (A)
5. The earliest available work of the Sangam Tamils is—
(A) Pattinappalai
(B) Tirumurugarruppadai
(C) Maduraikanchi
(D) Tolkappiyam
Ans : (D)
(A) Pattinappalai
(B) Tirumurugarruppadai
(C) Maduraikanchi
(D) Tolkappiyam
Ans : (D)
6. The Mahavir belonged to the clan—
(A) Kalams
(B) Bhaggas
(C) Lichhivis
(D) Bulis
Ans : (C)
(A) Kalams
(B) Bhaggas
(C) Lichhivis
(D) Bulis
Ans : (C)
7. The Jain text which contains the biographies of the Tirthankaras is known as—
(A) Bhagwatisutra
(B) Uvasagadasao
(C) Adi Purana
(D) Kalpasutra
Ans : (D)
(A) Bhagwatisutra
(B) Uvasagadasao
(C) Adi Purana
(D) Kalpasutra
Ans : (D)
8. The first Buddhist Sangeeti (conference) was held at—
(A) Vaishali
(B) Pataliputra
(C) Rajgriha
(D) Ujjain
Ans : (C)
(A) Vaishali
(B) Pataliputra
(C) Rajgriha
(D) Ujjain
Ans : (C)
9. The propounder of the Madhyamika Philosophy was—
(A) Bhadrabahu
(B) Parshwanath
(C) Sheelbhadra
(D) Nagarjuna
Ans : (D)
(A) Bhadrabahu
(B) Parshwanath
(C) Sheelbhadra
(D) Nagarjuna
Ans : (D)
10. The rules of Buddhist monistic life are laid down, primarily, in—
(A) Tripitaka
(B) Vinayapitaka
(C) Abhidhammapitaka
(D) Suttapitaka
Ans : (B)
(A) Tripitaka
(B) Vinayapitaka
(C) Abhidhammapitaka
(D) Suttapitaka
Ans : (B)
11. The battle between Alexander and Porus took place on the bank of river—
(A) Sutlej
(B) Ravi
(C) Jhelum
(D) Ganga
Ans : (C)
(A) Sutlej
(B) Ravi
(C) Jhelum
(D) Ganga
Ans : (C)
12. The first Persian ruler who occupied part of Indian Territory was—
(A) Cyrus
(B) Darius I
(C) Cambyses
(D) Xerxes
Ans : (B)
(A) Cyrus
(B) Darius I
(C) Cambyses
(D) Xerxes
Ans : (B)
13. Alexander remained in India for—
(A) 29 months
(B) 39 months
(C) 19 months
(D) 10 months
Ans : (C)
(A) 29 months
(B) 39 months
(C) 19 months
(D) 10 months
Ans : (C)
14. Gedrosia corresponds to modern—
(A) Baluchistan
(B) Lahore
(C) Multan
(D) Peshawar
Ans : (A)
(A) Baluchistan
(B) Lahore
(C) Multan
(D) Peshawar
Ans : (A)
15. Which of the following statements is not true ?
(A) Formal accession of Asoka was very probably delayed
(B) The fifth rock edict proves the existence of Harems of Asoka’s brothers
(C) Asoka held the viceroyalty of Taxila and Ujjain in the reign of Bindusara
(D) Asoka was the younger brother of Bindusara
Ans : (D)
(A) Formal accession of Asoka was very probably delayed
(B) The fifth rock edict proves the existence of Harems of Asoka’s brothers
(C) Asoka held the viceroyalty of Taxila and Ujjain in the reign of Bindusara
(D) Asoka was the younger brother of Bindusara
Ans : (D)
16. The nirvasita (excluded) and anirvasita (not excluded) Shudras have been referred to—
(A) in the Nirukta of Yaska
(B) in the Ashtadhyayi of Panini
(C) in the Arthashastra of Kautilya
(D) None of the above
Ans : (D)
(A) in the Nirukta of Yaska
(B) in the Ashtadhyayi of Panini
(C) in the Arthashastra of Kautilya
(D) None of the above
Ans : (D)
17. The first translator of Mahabharata into Tamil was—
(A) Perundevanar
(B) Kamban
(C) Sundaramurthi
(D) Bharavi
Ans : (A)
(A) Perundevanar
(B) Kamban
(C) Sundaramurthi
(D) Bharavi
Ans : (A)
18 Which one of the following inscriptions of Asoka refers to the grant of concession in land revenue to a village ?
(A) Lumbini Pillar edict
(B) Sarnath Pillar edict
(C) Girnar Rock edict
(D) Sanchi Pillar edict
Ans : (A)
(A) Lumbini Pillar edict
(B) Sarnath Pillar edict
(C) Girnar Rock edict
(D) Sanchi Pillar edict
Ans : (A)
19. Who of the following was not a patron of Jainism ?
(A) Bimbisara
(B) Kharvela
(C) Kanishka
(D) Chandragupta Maurya
Ans : (A)
(A) Bimbisara
(B) Kharvela
(C) Kanishka
(D) Chandragupta Maurya
Ans : (A)
20. Who was the ambassador in the Court of Bindusara ?
(A) Machiavelli
(B) Megasthenes
(C) Deimachus
(D) Antiochus I
Ans : (C)
(A) Machiavelli
(B) Megasthenes
(C) Deimachus
(D) Antiochus I
Ans : (C)
21. To propagate his Dhamma, Asoka used the services of—
(A) Rajukas
(B) Pradeshikas
(C) Yuktas
(D) All of these
Ans : (D)
(A) Rajukas
(B) Pradeshikas
(C) Yuktas
(D) All of these
Ans : (D)
22. The last king of Mauryan empire was—
(A) Devavarman
(B) Brihadrath
(C) Kunala
(D) Shalishuk
Ans : (B)
(A) Devavarman
(B) Brihadrath
(C) Kunala
(D) Shalishuk
Ans : (B)
23. The historian Kalhan was—
(A) Buddhist
(B) Brahmin
(C) Jain
(D) None of these
Ans : (B)
(A) Buddhist
(B) Brahmin
(C) Jain
(D) None of these
Ans : (B)
24 Founder of the Satvahana dynasty was—
(A) Shatkarni I
(B) Simuka
(C) Shatkarni II
(D) Rudradaman I
Ans : (B)
(A) Shatkarni I
(B) Simuka
(C) Shatkarni II
(D) Rudradaman I
Ans : (B)
25. Yen-Kao-Chen is generally known as—
(A) Kadphises I
(B) Kadphises II
(C) Kanishka
(D) Vasishka
Ans : (B)
(A) Kadphises I
(B) Kadphises II
(C) Kanishka
(D) Vasishka
Ans : (B)
26. The writer of the ‘Kalpasutra’ was—
(A) Simuka
(B) Panini
(C) Bhadrabahu
(D) Patanjali
Ans : (C)
(A) Simuka
(B) Panini
(C) Bhadrabahu
(D) Patanjali
Ans : (C)
27. The writer of the ‘Brihatkatha’ was—
(A) Dattamitra
(B) Gudadhya
(C) Bhadrabahu
(D) Sarvavarman
Ans : (B)
(A) Dattamitra
(B) Gudadhya
(C) Bhadrabahu
(D) Sarvavarman
Ans : (B)
28. According to tradition Kashyapa Matanga introduced Buddhism to—
(A) China
(B) Kashmir
(C) Ceylon
(D) Gandhar
Ans : (A)
(A) China
(B) Kashmir
(C) Ceylon
(D) Gandhar
Ans : (A)
29. Which one of the following indicates the correct chronological order of era in India ?
(A) Gupta—Harsha—Vikram—Shaka
(B) Vikram—Harsha—Gupta—Shaka
(C) Gupta—Shaka—Vikram—Harsha
(D) Vikram—Shaka—Gupta—Harsha
Ans : (D)
(A) Gupta—Harsha—Vikram—Shaka
(B) Vikram—Harsha—Gupta—Shaka
(C) Gupta—Shaka—Vikram—Harsha
(D) Vikram—Shaka—Gupta—Harsha
Ans : (D)
30. During Pre-Gupta period what was Kahapan ?
(A) An office
(B) A luxury item
(C) A coin
(D) A port
Ans : (C)
(A) An office
(B) A luxury item
(C) A coin
(D) A port
Ans : (C)
31. Which port was known to the author of “Periplus of the Erithrian Sea” as Padouke ?
(A) Tamralipti
(B) Arikmedu
(C) Broach
(D) Cochin
Ans : (B)
(A) Tamralipti
(B) Arikmedu
(C) Broach
(D) Cochin
Ans : (B)
32 Chandragupta-II married his daughter Prabhavati to—
(A) Rudrasena-I
(B) Rudrasena-II
(C) Agnimitra
(D) Nagsena
Ans : (B)
(A) Rudrasena-I
(B) Rudrasena-II
(C) Agnimitra
(D) Nagsena
Ans : (B)
33. Which of the following law givers of the post-Gupta period declared that Sudras were not slaves by nature ?
(A) Medhatithi
(B) Vigynaeshwar
(C) Narad
(D) Jimutwahan
Ans : (A)
(A) Medhatithi
(B) Vigynaeshwar
(C) Narad
(D) Jimutwahan
Ans : (A)
34. Who was the founder of Gahadwala dynasty who made Kannauj the main centre of his power ?
(A) Jaichandra
(B) Vijaychandra
(C) Chandradev
(D) Govind
Ans : (C)
(A) Jaichandra
(B) Vijaychandra
(C) Chandradev
(D) Govind
Ans : (C)
35. Which of the following Rashtrakut kings defeated the Pratihar ruler Nagabhatta I ?
(A) Indra II
(B) Krishna III
(C) Amoghvarsha I
(D) Govind III
Ans : (D)
(A) Indra II
(B) Krishna III
(C) Amoghvarsha I
(D) Govind III
Ans : (D)
36. Who among the following rulers patronized Jayadev, the composer of ‘Geetgovinda’ ?
(A) Laxman Sen
(B) Kharvel
(C) Kumarpala
(D) Shashank
Ans : (A)
(A) Laxman Sen
(B) Kharvel
(C) Kumarpala
(D) Shashank
Ans : (A)
37. Who out of the following ousted Jainism from Mysore ?
(A) Naynars
(B) Lingayats
(C) Alwars
(D) Shankaracharya
Ans : (D)
(A) Naynars
(B) Lingayats
(C) Alwars
(D) Shankaracharya
Ans : (D)
38. Which was the word used for the royal military troops of the Cholas ?
(A) Kattupaddi
(B) Kaikkolar
(C) Bhrtaka
(D) Kadgham
Ans : (B)
(A) Kattupaddi
(B) Kaikkolar
(C) Bhrtaka
(D) Kadgham
Ans : (B)
39. The Chola rulers undertook extensive land survey to ascertain—
(A) Right of ownership
(B) Government’s share of revenue
(C) Production of grains
(D) Limit of the sources of irrigation
Ans : (B)
(A) Right of ownership
(B) Government’s share of revenue
(C) Production of grains
(D) Limit of the sources of irrigation
Ans : (B)
40. Which of the following taxes of Chola period was for educational purpose ?
(A) Devadana
(B) Salabhoga
(C) Brahmadeva
(D) Sarvamanya
Ans : (A)
(A) Devadana
(B) Salabhoga
(C) Brahmadeva
(D) Sarvamanya
Ans : (A)
41. The writer of Tabqat-i-Nasiri was—
(A) Barani
(B) Nizamuddin
(C) Minhaj-us-Siraj
(D) Isami
Ans : (C)
(A) Barani
(B) Nizamuddin
(C) Minhaj-us-Siraj
(D) Isami
Ans : (C)
42. The following works were written by Ziauddin Barani—
(A) Tarikh-i-Firozshahi and Qiranussadain
(B) Fatwa-i-Jahandari and Ashiqa
(C) Tarikh-i-Firozshahi and Fatwa-i-Jahandari
(D) Futuhus-salatin and Tarikhi-Firozshahi
Ans : (C)
(A) Tarikh-i-Firozshahi and Qiranussadain
(B) Fatwa-i-Jahandari and Ashiqa
(C) Tarikh-i-Firozshahi and Fatwa-i-Jahandari
(D) Futuhus-salatin and Tarikhi-Firozshahi
Ans : (C)
43. Which of the following books were written by Amir Khusro ?
(A) Ashiqa, Qiranussadain, Khazain-ul-Futuh
(B) Qiranussadain, Ashiqa, Tarikh-i-Mubarakshahi
(C) Khazainul Futuh, Tarikh-i-Mubarakshahi, Ashiqa
(D) Tarikh-i-Mubarakshahi, Nuh-i-Siphr, Ashiqa
Ans : (A)
(A) Ashiqa, Qiranussadain, Khazain-ul-Futuh
(B) Qiranussadain, Ashiqa, Tarikh-i-Mubarakshahi
(C) Khazainul Futuh, Tarikh-i-Mubarakshahi, Ashiqa
(D) Tarikh-i-Mubarakshahi, Nuh-i-Siphr, Ashiqa
Ans : (A)
44. Who wrote ‘Qanun-i-Humayuni’ ?
(A) Gulbadan Begum
(B) Yahya
(C) Khwandmir
(D) Nizamuddin
Ans : (C)
(A) Gulbadan Begum
(B) Yahya
(C) Khwandmir
(D) Nizamuddin
Ans : (C)
45. Which of the following books was written by Ishwardas Nagar ?
(A) Futuhat-i-Alamgiri
(B) Bir Binod
(C) Chhatra Prakash
(D) Ahkam-i-Alamgiri
Ans : (A)
(A) Futuhat-i-Alamgiri
(B) Bir Binod
(C) Chhatra Prakash
(D) Ahkam-i-Alamgiri
Ans : (A)
46. With whom of the following Muhammad Ghori aligned against Khusrau Shah ?
(A) King of Gujarat
(B) King of Multan
(C) King of Peshawar
(D) King of Jammu
Ans : (D)
(A) King of Gujarat
(B) King of Multan
(C) King of Peshawar
(D) King of Jammu
Ans : (D)
47. At the time of Muhammad Ghori’s invasion against Prithviraj Chauhan who of the following ruled Kannauj ?
(A) The Chandellas
(B) The Pratihars
(C) The Palas
(D) The Gahadwalas
Ans : (D)
(A) The Chandellas
(B) The Pratihars
(C) The Palas
(D) The Gahadwalas
Ans : (D)
48. Who of the following contested with Qutubuddin Aibak for Punjab ?
(A) Ikhtiyaruddin
(B) Tajuddin Yaldauz
(C) Nasiruddin Qubacha
(D) None of these
Ans : (B)
(A) Ikhtiyaruddin
(B) Tajuddin Yaldauz
(C) Nasiruddin Qubacha
(D) None of these
Ans : (B)
49. Who were the Nav Musalmans of the following ?
(A) Descendants of Mongols who settled near Delhi and embraced Islam
(B) Hindu converts to Islam
(C) Khalji Sultans
(D) Ilbari Sultans
Ans : (A)
(A) Descendants of Mongols who settled near Delhi and embraced Islam
(B) Hindu converts to Islam
(C) Khalji Sultans
(D) Ilbari Sultans
Ans : (A)
50. Who was appointed as ambassador to China during the time of Mohammad bin Tughlaq ?
(A) Barbosa
(B) Barani
(C) Ibn Batutah
(D) Abdur Razzak
Ans : (C)
(A) Barbosa
(B) Barani
(C) Ibn Batutah
(D) Abdur Razzak
Ans : (C)
51. Bahlul Lodi’s significant achievement was the successful war against the underwritten kingdom of—
(A) Mewat
(B) Jaunpur
(C) Chandwar
(D) Sambhal
Ans : (B)
(A) Mewat
(B) Jaunpur
(C) Chandwar
(D) Sambhal
Ans : (B)
52. Rulers of which kingdom built Atala Masjid and Lal Darwaza Masjid ?
(A) Bengal
(B) Khandesh
(C) Malwa
(D) Jaunpur
Ans : (D)
(A) Bengal
(B) Khandesh
(C) Malwa
(D) Jaunpur
Ans : (D)
53. Rai Bharmal wrote on Muslim Literary traditions in the following language—
(A) Persian
(B) Sanskrit
(C) Arabic
(D) Turkish
Ans : (A)
(A) Persian
(B) Sanskrit
(C) Arabic
(D) Turkish
Ans : (A)
54. ‘Chaitanya Charitamrita’ was authored by—
(A) Wasweshwara
(B) Madhav
(C) Ramanand
(D) Krishnadas Kaviraj
Ans : (D)
(A) Wasweshwara
(B) Madhav
(C) Ramanand
(D) Krishnadas Kaviraj
Ans : (D)
55. Who succeeded Nizamuddin Aulia ?
(A) Sheikh Farid
(B) Sheikh Nasiruddin Chiraghi-Delhi
(C) Sheikh Salim Chishti
(D) None of the above
Ans : (B)
(A) Sheikh Farid
(B) Sheikh Nasiruddin Chiraghi-Delhi
(C) Sheikh Salim Chishti
(D) None of the above
Ans : (B)
56. Raidas, Sena and Kabir were the followers of—
(A) Namdeo
(B) Ramanuj
(C) Vallabhacharya
(D) Ramanand
Ans : (D)
(A) Namdeo
(B) Ramanuj
(C) Vallabhacharya
(D) Ramanand
Ans : (D)
57. When was Vijayanagar visited by Abdurrajjak ?
(A) 1443
(B) 1433
(C) 1423
(D) 1427
Ans : (A)
(A) 1443
(B) 1433
(C) 1423
(D) 1427
Ans : (A)
58. Tuluva dynasty was founded by—
(A) Narasa Nasyaka
(B) Immadi Narsimha
(C) Vir Narsimha
(D) None of these
Ans : (C)
(A) Narasa Nasyaka
(B) Immadi Narsimha
(C) Vir Narsimha
(D) None of these
Ans : (C)
59. Who founded the independent Bahamani kingdom in South India ?
(A) Abu Muzaffar Alauddin Bahmanshah
(B) Mujahid Shah
(C) Muhammad Shah I
(D) Adil Shah
Ans : (A)
(A) Abu Muzaffar Alauddin Bahmanshah
(B) Mujahid Shah
(C) Muhammad Shah I
(D) Adil Shah
Ans : (A)
60. Who founded the independent Muslim kingdom of Malwa ?
(A) Hoshangshah
(B) Mahmudshah
(C) Nasiruddin
(D) Dilawarkhan
Ans : (D)
(A) Hoshangshah
(B) Mahmudshah
(C) Nasiruddin
(D) Dilawarkhan
Ans : (D)
61. Babur had three wives. Which one of the following was not his wife ?
(A) Maham
(B) Gulrus
(C) Gulbadan
(D) Dilbar
Ans : (C)
(A) Maham
(B) Gulrus
(C) Gulbadan
(D) Dilbar
Ans : (C)
62. Who was Mehdi Khwaza ?
(A) Ruler of Bihar
(B) Prime Minister of Ibrahim Lodi
(C) Brother-in-law of Humayun
(D) Brother of Babur
Ans : (C)
(A) Ruler of Bihar
(B) Prime Minister of Ibrahim Lodi
(C) Brother-in-law of Humayun
(D) Brother of Babur
Ans : (C)
63. Humayun ascended the throne at Agra on—
(A) 7th January 1530
(B) 29th December 1530
(C) 23rd September 1530
(D) 16th February 1530
Ans : (B)
(A) 7th January 1530
(B) 29th December 1530
(C) 23rd September 1530
(D) 16th February 1530
Ans : (B)
64. Which of the following statements is true of the Sher Shah Suri ?
(A) He was a fanatic Muslim
(B) He was a staunch Muslim but not a fanatic
(C) He was a staunch Muslim and ill-treated Hindus
(D) He was intolerant towards other religions
Ans : (B)
(A) He was a fanatic Muslim
(B) He was a staunch Muslim but not a fanatic
(C) He was a staunch Muslim and ill-treated Hindus
(D) He was intolerant towards other religions
Ans : (B)
65. Which out of the following was not one of the purposes of ‘Sarais’ built during Sher Shah ?
(A) Post-house
(B) For travellers
(C) For officers
(D) Warehouse for arms and ammunition
Ans : (D)
(A) Post-house
(B) For travellers
(C) For officers
(D) Warehouse for arms and ammunition
Ans : (D)
66. Who was not appointed as Vazir during Akbar’s reign ?
(A) Bahadurkhan Uzbeg
(B) Shamsuddin Atkakhan
(C) Todarmal
(D) Nizamuddin Khalifa
Ans : (A)
(A) Bahadurkhan Uzbeg
(B) Shamsuddin Atkakhan
(C) Todarmal
(D) Nizamuddin Khalifa
Ans : (A)
67. Which of the following pairs is incorrect ?
(A) Akbar—Ralph Fich
(B) Darashikoh—Manucci
(C) Jahangir—Sir Thomas Roe
(D) Shah Jahan—Jourdon
Ans : (D)
(A) Akbar—Ralph Fich
(B) Darashikoh—Manucci
(C) Jahangir—Sir Thomas Roe
(D) Shah Jahan—Jourdon
Ans : (D)
68. Which of the following statements is true of Akbar’s policy towards the Hindus ?
(A) He abolished the pilgrim tax but not the Jaziya
(B) He abolished the Jaziya, but not the pilgrim tax
(C) He abolished both the Jaziya and the pilgrim tax
(D) He neither abolished the pilgrim tax nor the Jaziya
Ans : (C)
(A) He abolished the pilgrim tax but not the Jaziya
(B) He abolished the Jaziya, but not the pilgrim tax
(C) He abolished both the Jaziya and the pilgrim tax
(D) He neither abolished the pilgrim tax nor the Jaziya
Ans : (C)
69 Who was the author of ‘Nuskhai-Dilkusha’ ?
(A) Khafi Khan
(B) Murshidkuli Khan
(C) Abul Fazl
(D) Bhimsen Burhanpuri
Ans : (D)
(A) Khafi Khan
(B) Murshidkuli Khan
(C) Abul Fazl
(D) Bhimsen Burhanpuri
Ans : (D)
70. Guru Govind Singh was killed in 1708 at—
(A) Amritsar
(B) Keeratpur
(C) Nanded
(D) Anandpur
Ans : (C)
(A) Amritsar
(B) Keeratpur
(C) Nanded
(D) Anandpur
Ans : (C)
71. Mir Sayyed Ali and Abdusamad were the court painter during the time of—
(A) Humayun, Akbar
(B) Akbar, Jahangir
(C) Jahangir, Shah Jahan
(D) Shah Jahan, Aurangzeb
Ans : (A)
(A) Humayun, Akbar
(B) Akbar, Jahangir
(C) Jahangir, Shah Jahan
(D) Shah Jahan, Aurangzeb
Ans : (A)
72. Which of the following elements was not found in Akbar’s architecture ?
(A) Use of red sandstone
(B) Hindu elements
(C) Foliated arches
(D) Charbagh surrounding the tombs
Ans : (C)
(A) Use of red sandstone
(B) Hindu elements
(C) Foliated arches
(D) Charbagh surrounding the tombs
Ans : (C)
73. Who composed ‘Ganga Lahri’ ?
(A) Tulsidas
(B) Surdas
(C) Panditraj Jagannath
(D) Haridasa
Ans : (C)
(A) Tulsidas
(B) Surdas
(C) Panditraj Jagannath
(D) Haridasa
Ans : (C)
74. Which of the following was not a silver coin during Akbar ?
(A) Jalal
(B) Dam
(C) Darab
(D) Pandau
Ans : (B)
(A) Jalal
(B) Dam
(C) Darab
(D) Pandau
Ans : (B)
75. Which of the following revolts had agrarian causes at its root ?
(A) Rajput revolt
(B) Satnami and Jat revolt
(C) Sikh revolt
(D) Maratha revolt
Ans : (B)
(A) Rajput revolt
(B) Satnami and Jat revolt
(C) Sikh revolt
(D) Maratha revolt
Ans : (B)
76. From whom Shahji received the jagir of Poona ?
(A) Mughals
(B) Adilshah
(C) Nizamshahi
(D) Portuguese
Ans : (B)
(A) Mughals
(B) Adilshah
(C) Nizamshahi
(D) Portuguese
Ans : (B)
77. What is ‘Mokasa’ ?
(A) Jagir
(B) Religious practice
(C) Cavalry
(D) Religious endowment
Ans : (A)
(A) Jagir
(B) Religious practice
(C) Cavalry
(D) Religious endowment
Ans : (A)
78. Who was not alive at the time of Shivaji’s Coronation ?
(A) Ganga Bhatt
(B) Tukaram
(C) Ramdas
(D) Dadaji Konddeva
Ans : (D)
(A) Ganga Bhatt
(B) Tukaram
(C) Ramdas
(D) Dadaji Konddeva
Ans : (D)
79. Which of the following Peshwas is connected with the treaty of Sagola ?
(A) Balaji Bajirao
(B) Balaji Vishwanath
(C) Bajirao I
(D) Bajirao II
Ans : (A)
(A) Balaji Bajirao
(B) Balaji Vishwanath
(C) Bajirao I
(D) Bajirao II
Ans : (A)
80. In which year Ahilyabai Holkar breathed her last ?
(A) 1792
(B) 1793
(C) 1794
(D) 1795
Ans : (D)
(A) 1792
(B) 1793
(C) 1794
(D) 1795
Ans : (D)
81. The French East India Company was formed in—
(A) 1664 AD
(B) 1660 AD
(C) 1656 AD
(D) 1680 AD
Ans : (A)
(A) 1664 AD
(B) 1660 AD
(C) 1656 AD
(D) 1680 AD
Ans : (A)
82. La Bourdonnais was the Governor of—
(A) Madras
(B) Pondicherry
(C) Mauritius
(D) None of these
Ans : (B)
(A) Madras
(B) Pondicherry
(C) Mauritius
(D) None of these
Ans : (B)
83. Mir Kasim removed his court from Calcutta to—
(A) Patna
(B) Dacca
(C) Monghir
(D) Purnea
Ans : (C)
(A) Patna
(B) Dacca
(C) Monghir
(D) Purnea
Ans : (C)
84. The battle of Wandiwash was fought between—
(A) English and the French
(B) English and the Marathas
(C) English and the Nawab of Carnatic
(D) English and Hyderali
Ans : (A)
(A) English and the French
(B) English and the Marathas
(C) English and the Nawab of Carnatic
(D) English and Hyderali
Ans : (A)
85. At the battle of Biddera the English crushed the power of—
(A) French
(B) Dutch
(C) Portuguese
(D) Danes
Ans : (B)
(A) French
(B) Dutch
(C) Portuguese
(D) Danes
Ans : (B)
86. The Treaty of Surat was concluded by the British with the following Maratha chief—
(A) Narayan Rao
(B) Madhav Rao
(C) Nana Phadnvis
(D) Raghoba
Ans : (D)
(A) Narayan Rao
(B) Madhav Rao
(C) Nana Phadnvis
(D) Raghoba
Ans : (D)
87. The triple alliance against Tipu was formed by Cornwallis consisted of the following—
(A) The English, Nizam and the Marathas
(B) The English, Nizam and Awadh
(C) The English, Nizam and Carnatic
(D) The English, Marathas and Carnatic
Ans : (A)
(A) The English, Nizam and the Marathas
(B) The English, Nizam and Awadh
(C) The English, Nizam and Carnatic
(D) The English, Marathas and Carnatic
Ans : (A)
88. In the Second Sikh War the decisive battle was fought at—
(A) Chilianwala
(B) Peshawar
(C) Gujarat
(D) Multan
Ans : (C)
(A) Chilianwala
(B) Peshawar
(C) Gujarat
(D) Multan
Ans : (C)
89. In the Third Maratha War, the English defeated Peshwa Bajirao II at—
(A) Mahidpur
(B) Sitabuldi
(C) Kirki
(D) Bassein
Ans : (D)
(A) Mahidpur
(B) Sitabuldi
(C) Kirki
(D) Bassein
Ans : (D)
90. The Treaty of Shrirangpattam took place in—
(A) 1791
(B) 1792
(C) 1793
(D) 1794
Ans : (D)
(A) 1791
(B) 1792
(C) 1793
(D) 1794
Ans : (D)
91. Which of the following states was not annexed to British Empire by Dalhousie under the doctrine of Lapse ?
(A) Baghat
(B) Nagpur
(C) Sambalpur
(D) Benaras
Ans : (D)
(A) Baghat
(B) Nagpur
(C) Sambalpur
(D) Benaras
Ans : (D)
92. Which one of the following rebellions is associated with Sidhu and Kanhu ?
(A) Munda Rebellion
(B) Kole Rebellion
(C) Santhal Rebellion
(D) Bhil Rebellion
Ans : (C)
(A) Munda Rebellion
(B) Kole Rebellion
(C) Santhal Rebellion
(D) Bhil Rebellion
Ans : (C)
93. The following officer was connected with the suppression of Thugee—
(A) Hastings
(B) Sleeman
(C) Bentinck
(D) Aukland
Ans : (C)
(A) Hastings
(B) Sleeman
(C) Bentinck
(D) Aukland
Ans : (C)
94. Which of the following British Officers was not in favour of annexation of Awadh ?
(A) Outram
(B) Napier
(C) Hugh Rose
(D) Sleeman
Ans : (D)
(A) Outram
(B) Napier
(C) Hugh Rose
(D) Sleeman
Ans : (D)
95. Charles Metcalf was the Governor General of India during—
(A) 1835-36
(B) 1839-40
(C) 1837-38
(D) 1832-33
Ans : (A)
(A) 1835-36
(B) 1839-40
(C) 1837-38
(D) 1832-33
Ans : (A)
96. Sindh was invaded during the following Governor General’s time—
(A) Lord Aukland
(B) Lord Ellenborough
(C) Lord Hardinge
(D) Lord Dalhousie
Ans : (B)
(A) Lord Aukland
(B) Lord Ellenborough
(C) Lord Hardinge
(D) Lord Dalhousie
Ans : (B)
97. The Second Burmese War was fought in the year—
(A) 1849
(B) 1850
(C) 1851
(D) 1852
Ans : (B)
(A) 1849
(B) 1850
(C) 1851
(D) 1852
Ans : (B)
98. Which one of the following Acts abolished the trading rights of the East India Company ?
(A) Regulating Act of 1773
(B) Charter Act of 1813
(C) Charter Act of 1833
(D) Charter Act of 1853
Ans : (B)
(A) Regulating Act of 1773
(B) Charter Act of 1813
(C) Charter Act of 1833
(D) Charter Act of 1853
Ans : (B)
99. Which one of the following pairs is not correctly matched ?
(A) Ryotwari Settlement : Madras
(B) Talukdari Settlement : Bombay
(C) Permanent Settlement : Bengal
(D) Mahalwari Settlement : North-Western Province
Ans : (B)
(A) Ryotwari Settlement : Madras
(B) Talukdari Settlement : Bombay
(C) Permanent Settlement : Bengal
(D) Mahalwari Settlement : North-Western Province
Ans : (B)
100. The gradual increase in rural indebtedness in India under the British rule was due to—
1. Fragmentation of Landholdings
2. Decline of cottage industries
3. Lack of development of irrigational facilities
4. Introduction of cash crops Which of these are correct ?
(A) 1, 2 and 3
(B) 2 and 4
(C) 1, 3 and 4
(D) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans : (D)
1. Fragmentation of Landholdings
2. Decline of cottage industries
3. Lack of development of irrigational facilities
4. Introduction of cash crops Which of these are correct ?
(A) 1, 2 and 3
(B) 2 and 4
(C) 1, 3 and 4
(D) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans : (D)
101. At Lucknow the revolt of 1857 broke out on—
(A) May 30, 1857
(B) June 4, 1857
(C) May 15, 1857
(D) June 15, 1857
Ans : (B)
(A) May 30, 1857
(B) June 4, 1857
(C) May 15, 1857
(D) June 15, 1857
Ans : (B)
102. The Asiatic Society of Bengal in Calcutta was founded by—
(A) Raja Ram Mohan Roy
(B) Sir Williams Jones
(C) Warren Hastings
(D) Keshabchandra Sen
Ans : (B)
(A) Raja Ram Mohan Roy
(B) Sir Williams Jones
(C) Warren Hastings
(D) Keshabchandra Sen
Ans : (B)
103. The Theosophical Society allied itself to the—
(A) Christian revival movement
(B) Islamic revival movement
(C) Hindu revival movement
(D) All of these
Ans : (C)
(A) Christian revival movement
(B) Islamic revival movement
(C) Hindu revival movement
(D) All of these
Ans : (C)
104. Which of the following statements about the Ramakrishna Mission is wrong ?
(A) It held the pure Vedantic doctrine as its ideal
(B) It aimed at the development of the highest spirituality in man
(C) It prohibited the worship of images
(D) It recognised modern developments in Science and Technology
Ans : (C)
(A) It held the pure Vedantic doctrine as its ideal
(B) It aimed at the development of the highest spirituality in man
(C) It prohibited the worship of images
(D) It recognised modern developments in Science and Technology
Ans : (C)
105. Fifth Session of the Indian National Congress was held in 1889 at—
(A) Calcutta
(B) Madras
(C) Bombay
(D) Dacca
Ans : (C)
(A) Calcutta
(B) Madras
(C) Bombay
(D) Dacca
Ans : (C)
106. The moderates and extremists were united in the Congress Session of—
(A) Lahore
(B) Bombay
(C) Allahabad
(D) Lucknow
Ans : (D)
(A) Lahore
(B) Bombay
(C) Allahabad
(D) Lucknow
Ans : (D)
107. Who among the following was not in Khilafat Committee ?
(A) Majhar ul Haq
(B) Hasrat Mohani
(C) Maulana Shauqat Ali
(D) Hakim Azmalkhan
Ans : (A)
(A) Majhar ul Haq
(B) Hasrat Mohani
(C) Maulana Shauqat Ali
(D) Hakim Azmalkhan
Ans : (A)
108. Who among the following was the president of All India Trade Union Congress in 1929 ?
(A) M. N. Roy
(B) N. M. Joshi
(C) Jawaharlal Nehru
(D) Jayaprakash Narayan
Ans : (B)
(A) M. N. Roy
(B) N. M. Joshi
(C) Jawaharlal Nehru
(D) Jayaprakash Narayan
Ans : (B)
109. Swaraj Party was formed by—
(A) C. R. Das
(B) Motilal Nehru
(C) Jawaharlal Nehru
(D) C. R. Das and Motilal Nehru
Ans : (D)
(A) C. R. Das
(B) Motilal Nehru
(C) Jawaharlal Nehru
(D) C. R. Das and Motilal Nehru
Ans : (D)
110. ‘Lucknow Pact’ was concluded between—
(A) Congress and the British Government
(B) Muslim League and the British Government
(C) Congress and the Muslim League
(D) Congress, the Muslim League and the British Government
Ans : (C)
(A) Congress and the British Government
(B) Muslim League and the British Government
(C) Congress and the Muslim League
(D) Congress, the Muslim League and the British Government
Ans : (C)
111. An All Party Conference appointed a sub-committee with Ali Imam, Tejbahadur Sapru and Subhash Bose. Who was presiding this subcommittee ?
(A) Maulana Azad
(B) Vallabh Bhai Patel
(C) Madan Mohan Malviya
(D) Motilal Nehru
Ans : (D)
(A) Maulana Azad
(B) Vallabh Bhai Patel
(C) Madan Mohan Malviya
(D) Motilal Nehru
Ans : (D)
112. Who among the following participated in all the three Round Table Conferences ?
(A) Madan Mohan Malviya
(B) B. R. Ambedkar
(C) Sardar Patel
(D) None of these
Ans : (B)
(A) Madan Mohan Malviya
(B) B. R. Ambedkar
(C) Sardar Patel
(D) None of these
Ans : (B)
113. Which of the following pairs is correct ?
(A) Ramprasad Bismil : Second Lahore Conspiracy Case
(B) Surya Sen : Chatgaon Case
(C) Bhagat Singh : Kakori Conspiracy Case
(D) Chandrashekhar Azad : Delhi Bomb Case
Ans : (B)
(A) Ramprasad Bismil : Second Lahore Conspiracy Case
(B) Surya Sen : Chatgaon Case
(C) Bhagat Singh : Kakori Conspiracy Case
(D) Chandrashekhar Azad : Delhi Bomb Case
Ans : (B)
114. When were the Congress Governments formed in seven out of eleven provinces ?
(A) July 1935
(B) July 1936
(C) July 1937
(D) July 1938
Ans : (C)
(A) July 1935
(B) July 1936
(C) July 1937
(D) July 1938
Ans : (C)
115. Which of the following pairs is correct ?
(A) Chelmsford : Rowlatt Act
(B) Lord Reading : Delhi Darbar
(C) Lord Willington : Arriving of Prince of Wales in India
(D) Lord Hardinge : II Round Table Conference
Ans : (A)
(A) Chelmsford : Rowlatt Act
(B) Lord Reading : Delhi Darbar
(C) Lord Willington : Arriving of Prince of Wales in India
(D) Lord Hardinge : II Round Table Conference
Ans : (A)
116. Subhash Chandra Bose inaugurated the government of Free India at—
(A) Burma
(B) Japan
(C) Germany
(D) Singapore
Ans : (D)
(A) Burma
(B) Japan
(C) Germany
(D) Singapore
Ans : (D)
117. In December 1931 two school girl students killed the District Judge in Komilla by shooting—
(A) Suniti Choudhary and Bina Das
(B) Shanti Ghosh and Suniti Choudhary
(C) Bina Das and Kalpana Datta
(D) Kalpana Datta and Shanti Ghosh
Ans : (B)
(A) Suniti Choudhary and Bina Das
(B) Shanti Ghosh and Suniti Choudhary
(C) Bina Das and Kalpana Datta
(D) Kalpana Datta and Shanti Ghosh
Ans : (B)
118. Which of the following pairs is correct ?
(A) Chuar Revolt : Orissa
(B) Sanyasi Revolt : Bihar
(C) Parlakhemundi Revolt : Orissa
(D) Rampa Revolt : Karnatak
Ans : (B)
(A) Chuar Revolt : Orissa
(B) Sanyasi Revolt : Bihar
(C) Parlakhemundi Revolt : Orissa
(D) Rampa Revolt : Karnatak
Ans : (B)
119. The following countries undertook the responsibility of organising the Bandung Conference—
(A) Indonesia, Burma, Cambodia
(B) India, Burma, Indonesia
(C) Sri Lanka, Indonesia, Cambodia
(D) China, Japan, Thailand
Ans : (B)
(A) Indonesia, Burma, Cambodia
(B) India, Burma, Indonesia
(C) Sri Lanka, Indonesia, Cambodia
(D) China, Japan, Thailand
Ans : (B)
120. Which of the following Articles of Indian Constitution declares it is a primary duty of the state to raise the level of nutrition and the standard of living of its people and the “Improvement of the Public Health” ?
(A) Article 46
(B) Article 47
(C) Article 48
(D) Article 49
Ans : (B)
(A) Article 46
(B) Article 47
(C) Article 48
(D) Article 49
Ans : (B)
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
